What is pneumonia?
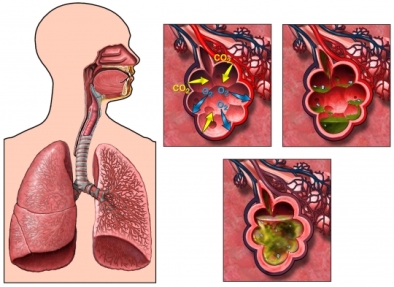
Pneumonia is an infection in one or both of the lungs caused by greater than 30 different sources including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and small germs. Therefore, it is important to identify the source of infection to choose the correct treatment.
The most common cause of viral pneumonia in adult is the flu virus. You can get pneumonia when your immune system becomes weak, or a germ is strong or large amount invades your body, or your body cannot filter germs from airways, or combination of previous causes. When germs invade the lungs’ air sacs (alveoli), alveoli become inflamed and fill up with fluid which cause symptoms of pneumonia.
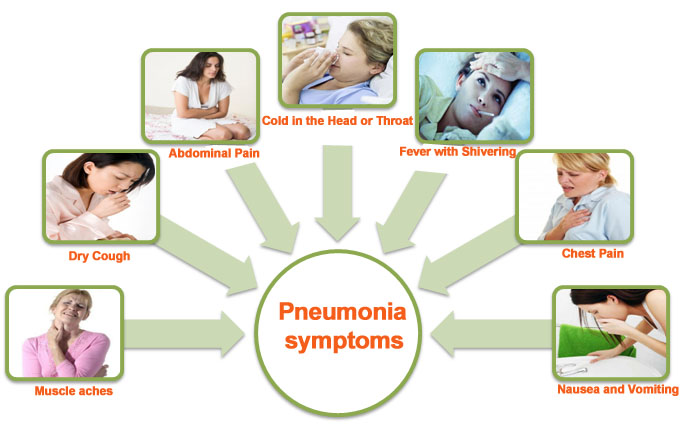
- Cough (new or increased)
- Increase production or change color of mucus
- Body temperature lower or higher than normal
- Fever (>100.9F or 38.3C)
- Low body temp (<96.1F or 35.6C)
- Shortness of breath
- Pain worsens when you breath, cough, or sneeze
- Altered mental status
- Hyperventilating
Risk factor for pneumonia
- Cigarette smoking
- Recent viral respiratory infection (i.e. flu) due to weakened immune system which could lead to complication of respiratory infection, pneumonia
- Chronic lung disease (i.e. COPD, bronciectasis, or cystic fibrosis)
- Resident in a nursing facility – setting is similar to hospital where many contagions are present and contagions are easy to spread
- Alcoholism
- Difficulty swallowing – can cause aspiration in which foreign objects can get through airway instead of esophagus lead to infection and inflammation of lung(s)
Should I be concerned?
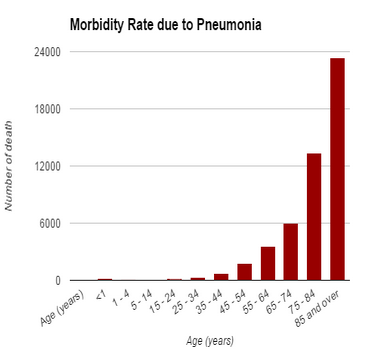
While many people completely recover from pneumonia, it could also be fatal. According to CDC, pneumonia and flu together is number 9 cause of death in the US
Risk factors for complications?
- Children <1 year or adults ≥65 years
- Chronic health conditions (i.e. diabetes, cirrhosis, etc)
- Other diseases or factors to weaken immune system (i.e. AIDs, transplant, cancer, asplenic, etc)
What are some complications?
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – a severe form of respiratory failure
- requires ventilator (a breathing machine)
- Lung abscesses
- Not common but serious complication of pneumonia
- Pockets of pus forms inside or around the lung which may require surgical drainage
- Sepsis
- uncontrolled inflammation of the body which may progress to widespread organ failure
How is it diagnosed?
- Symptoms + Chest X-ray
- Symptoms + Necessary laboratory findings
How can I feel better?
- Seek medical help first
- Stay hydrated and consume well balanced diet
- Analgesics or antipyretics
- acetaminophen or NSAIDs (i.e. Ibuprofen, Naproxen)
- Bed rest
Treatment of community acquired pneumonia
- Treatment course totally depends on the source of infection and severity
- Typical treatments include:
- Azithromycin for minimum 5 days
- High risk patients (with diabetes, chronic heart, lung, liver or kidney disease, alcoholism, cancer, asplenia, etc)
- Levaquin (Levofloxacin) for at least 5 days
- Avoid for kids (may cause cartilage damage) unless penicillin allergy and person with cardiac disease
- Augmentin + Z-Pak for minimum 5 days
Prevention
- Vaccines, vaccines vaccines!
- Don’t get the flu! Get a flu shot
- Protect yourselves against pneumococcal bacteria
- Quit smoking at any point of your life. Talk to your HP pharmacists about smoking cessation today
- Keep airways clean, cover your cough & sneeze, and clean your hands
How can HPP help?
- Vaccines
- Pneumonia shots are available all year long for anybody 18 years and older!
- Know your vaccine history. It will be helpful to determine which vaccine you should be getting
- Pneumonia shots are available all year long for anybody 18 years and older!
- Who should get Prevnar?
- If you are ≥65 years old and have not gotten Prevnar between age 19-64 or vaccine history is unknown
- Prevnar → 6 – 12 mos → Pneumovax
- Pneumovax → 1 year → Prevnar
- Two vaccines work together to produce the optimal antibody activity against pneumonia bugs4,5
- If you are ≥65 years old and have not gotten Prevnar between age 19-64 or vaccine history is unknown
- Flu season in the US begins as early as October and last until as late as May BUT it takes 2 weeks to produce enough antibody after vaccination
- Flu shots are available for age ≥14 years
- Get the flu shot as early as mid-September which will protect you for a year
What will happen in severe case of pneumonia?
- You should be treated in the hospital if you have severe signs and symptoms of pneumonia or if it gets worse while you are getting treated at home. (See risk & examples of complications)
Need help resuming back to normal life?
- HPP is participating in unique transition of care project (Project Harmony). When a patient is referred by a hospital, we ensure that
- Patient will get correct medicines at the proper time (we package the medicine in pill organizer)
- Medicine gets delivered (if requested by the patient)
- Patient should be seen by primary physician in 30 days to follow up recent hospital visit and make sure well-being of the patient
- Connect patient with a case manager to assist his/she at home
References:
- American Lung Association
www.lung.org/lung-disease/pneumonia
2. IDSA guideline
https://www.thoracic.org/statements/resources/mtpi/idsaats-cap.pd
3. 2013 Mortality rate
http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr64/nvsr64_02.pdf
4. Morbidity and mortality weekly report in 2014
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6337a4.htm
5. CDC vaccination schedule
http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/adult.html